Consent Directory for Common Medical Procedures
Consent is an extremely important part of medicine, particularly in the surgical specialties. When patients come seeking medical advice, they have the right to know the risks and complications of their treatments, as well as the relative frequencies.
Everyone aged 16 and older is assumed to have capacity (the ability to make informed decisions) unless proved otherwise. This includes anybody with dementia or a learning disability. If there is doubt, formal assessment for capacity needs to be carried out by a trained healthcare professional. This consists of:
1. Can the patient understand and retain information?
2. Can they weigh the pros and cons to make a decision?
3. Can they then communicate that decision?
If a patient is found to not have capacity, then healthcare professionals need to act in the patient's best interests, and in the UK we have a specific consent form for this (Consent Form 4). Some patients may have Advanced Directives or Lasting Power of Attorney, which will also impact on the consent process.
Consent for children needs to be obtained from a parent, but this is not an excuse not to involve the child in the decision.
In the UK, the GMC issue clear guidance on obtaining consent from patients (http://www.gmc-uk.org/guidance/ethical_guidance/consent_guidance_index.asp).
Some of the major principles to bear in mind:
1. No-one can take consent on behalf of an adult who has capacity.
2. The healthcare professional taking consent must be suitably qualified, should have
knowledge about the procedure/ treatment including its risks, complications, and likelihood of failure.
3. Consent can be verbal (a patient says yes to be examined), written (formal signature and documentation) or implied (a patient offering their arm when they attend for a blood test).
My hope is to make this post a one-stop directory for consent for the commoner surgical and invasive procedures. I will not list specific surgical speciality operations (e.g. nasal septoplasty), but focus on the procedures that a junior doctor in the UK might be expected to consent for (provided they meet the criteria listed above).
The complications common to ALL invasive procedures:
1. Bleeding
2. Infection
3. Pain
4. Failure of procedure
5. Anaesthetic complications (if general anaesthesia used)
The frequency of the above will depend on the procedure.
CARDIOVASCULAR
Angiography
(source)
Purpose: to visualise the internal anatomy of the coronary arteries and/or treat any blockages via stenting
Benefits: remove blockages, improve angina symptoms, obtain a diagnosis
Complications: pain, bleeding, infection + allergy to contrast, kidney damage from contrast, irregular heart rhythms (arrhythmias), damage to blood vessels, stroke
More Information: http://healthlibrary.epnet.com/GetContent.aspx?token=c5987b1e-add7-403a-b817-b3efe6109265&chunkiid=42307
RESPIRATORY
Chest drain insertion
(source)
Purpose: to drain fluid from the pleural cavity and improve breathing, obtain samples to get a diagnosis OR to remove air from the pleural cavity and treat a pneumothorax
Benefits: Remove air/ fluid, obtain a diagnosis
Complications: pain, bleeding, infection + damage to local structures including ribs, nerves, blood vessels, lung laceration, colon/ stomach injury, blockage of tube
More information: http://www.trauma.org/archive/thoracic/CHESTdrain.html
Aspiration of pleural fluid/ pleural tap
(source)
Purpose: to obtain samples of fluid in the pleural cavity
Benefits: obtain diagnosis, symptomatic relief
Complications: pain, bleeding, infection + damage to local structures including ribs, nerves, blood vessels, lung laceration
GASTRO
Upper GI endoscopy
(source)
Purpose: To directly visualise the oesophagus/ stomach/ duodenum for pathology and/or treat/ take biopsy samples for diagnosis
Benefits: obtain diagnosis, treat symptoms
Complications: pain, bleeding, infection + risk of perforation of oesophagus requiring surgical repair
Lower GI endoscopy (colonoscopy/ flexible sigmoidoscopy)
Purpose: To directly visualise the colon for pathology and/or treat/ take biopsy samples for diagnosis
Benefits: obtain diagnosis, treat symptoms
Complications: pain, bleeding, infection + risk of perforation of bowel
More info: http://healthlibrary.epnet.com/GetContent.aspx?token=c5987b1e-add7-403a-b817-b3efe6109265&chunkiid=14795
ORTHOPAEDIC
Joint aspiration
(source)
Purpose: To remove joint fluid
Benefits: Symptomatic relief, obtain diagnosis
Complications: pain, bleeding, infection + reaccumulation of fluid, damage to local nerves/ blood vessels/ tendons
Joint injection
Purpose: to inject treatment directly to site
Benefits: Symptomatic relief
Complications: pain, bleeding, infection + damage to local skin/ nerves/ blood vessels, tendon damage, tendon rupture, hypopigmentation of skin at injection site
More info: http://healthlibrary.epnet.com/GetContent.aspx?token=c5987b1e-add7-403a-b817-b3efe6109265&chunkiid=744873
OBSTETRIC/ GYNAECOLOGY
Caesarian (Cesarian) Section
Purpose: to delivery baby that cannot be delivered by normal means
Benefits: to deliver fetus
Complications: pain, bleeding, infection + blood clots, damage to bladder/ bowel requiring repair, hysterectomy, blood transfusion
More info: http://healthlibrary.epnet.com/GetContent.aspx?token=c5987b1e-add7-403a-b817-b3efe6109265&chunkiid=14798
Surgical evacuation of retained products of conception
Purpose: to remove retained products to prevent infection/ stop life-threatening bleeding
Benefits: remove products
Complications: pain, bleeding, infection + blood transfusion, risk of perforation of uterus, incomplete removal requiring further procedure, damage to cervix/ bladder/ bowel requiring repair
More info: http://www.qegateshead.nhs.uk/sites/default/files/users/user1/leaflets/IL362%20ERPC%20%28Evacuation%20of%20the%20Retained%20Products%20of%20Conception%29.pdf
GENERAL SURGERY
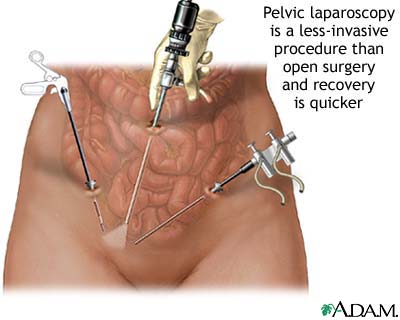
Laparoscopic procedure
(source)
Purpose: variable (e.g. laparoscopic appendicetomy to remove appendix, laparoscopic oophrectomy to remove ovaries etc)
Benefits: avoid open procedure, quicker recovery, fewer complications
Complications: pain, bleeding, infection + perforation of abdominal organs, damage to local vessels/ nerves, need to convert to open procedure
Think I should add more? Please suggest what other procedures you'd like to see listed!